1. Product IntroductionThe hydraulic pulping machine is used in the papermaking industry to disintegrate pulping boards, waste paper, waste paper boxes, and damaged paper. It achieves the purpose of crushing and dispersing through the mechanical action of the blades on the turntable and the tearing action introduced by the rotation of the turntable, which drives the middle concentration stirring cage.The metal trough hydraulic pulping machine consists of a vertical open metal trough, a blade turntable support, a rotor with a rubber transmission, a gate valve, and other components.Currently, the company's newly developed energy-saving pulping machine can double the output under the same volume and power conditions.
2. Working PrincipleThe main function of the vertical low-consistency hydraulic pulping machine is caused by the mechanical action of the turntable blades and the hydraulic shearing action generated by the rotor's rotation. As the rotor rotates, the pulp, paper material, and water are drawn in along the central axis and are rapidly ejected from the outer circumference of the rotor, forming a strong turbulent circulation. Due to the intense impact, tearing of the blades on the pulp, and the tremendous friction existing between layers of fluid with different speeds, the pulp blocks and paper materials are forcefully and effectively disintegrated in a liquid state. Any unbroken paper pieces and fiber bundles are further dispersed between the rotor blades and the screen plate, with the qualified pulp passing through specific-sized screen holes to flow out of the pulping machine.
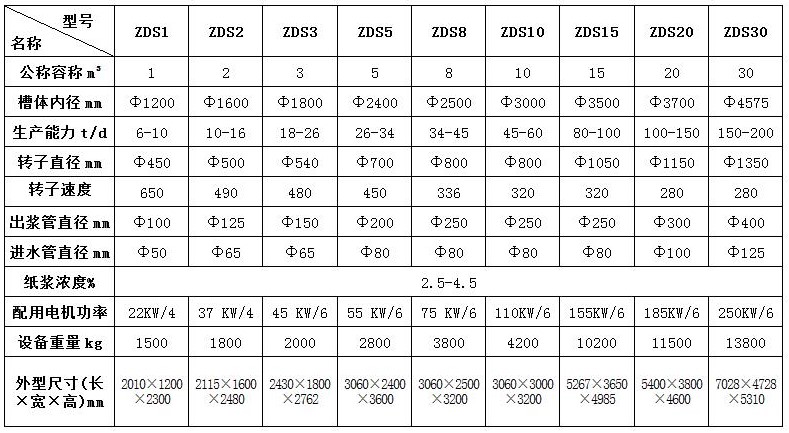
3. Parameter SelectionCurrently, the pulping machine is customized according to customer requirements, with a minimum of 160 liters and 0.5m³ for experimental equipment, and a maximum single unit capacity of 100m³. For machines exceeding 30 cubic meters, individual customization is required. For inquiries, please contact the company at 0536-6081238, and technical information will be sent separately to customers.
4. Parameter selection
(2) (7).jpg)

(2) (13).jpg)


(3) (1).jpg)
(3)_(2).jpg)
(2) (4).jpg)
(2) (5).jpg)
